2 + 2
5 - 2
5 * 2
6/21 Statistics and the Scientific Method
1.1 Motivation
In God we trust, all others must bring data.
Statistical thinking will one day be as necessary a qualification for efficient citizenship as the ability to read & write.
To call in the statistician after the experiment is done may be no more than asking him to perform a postmortem examination: he may be able to say what the experiment died of.
1.2 Introduction
- Statistics is the science concerned with using sample information to make inference about populations.
- Statistics is the science of uncertainty and variability.
- Statistics is the interpretation of Science
- Data Driven Decisions (3Ds)
1.3 Reasoning
- Deduction
- Reasoning from general to particular.
- Man is mortal. → Every human being is mortal.
- Induction
- Reasoning from particular to general.
1.4 Statistical Reasoning & Analysis
- Statistics is the science of uncertainty & variability
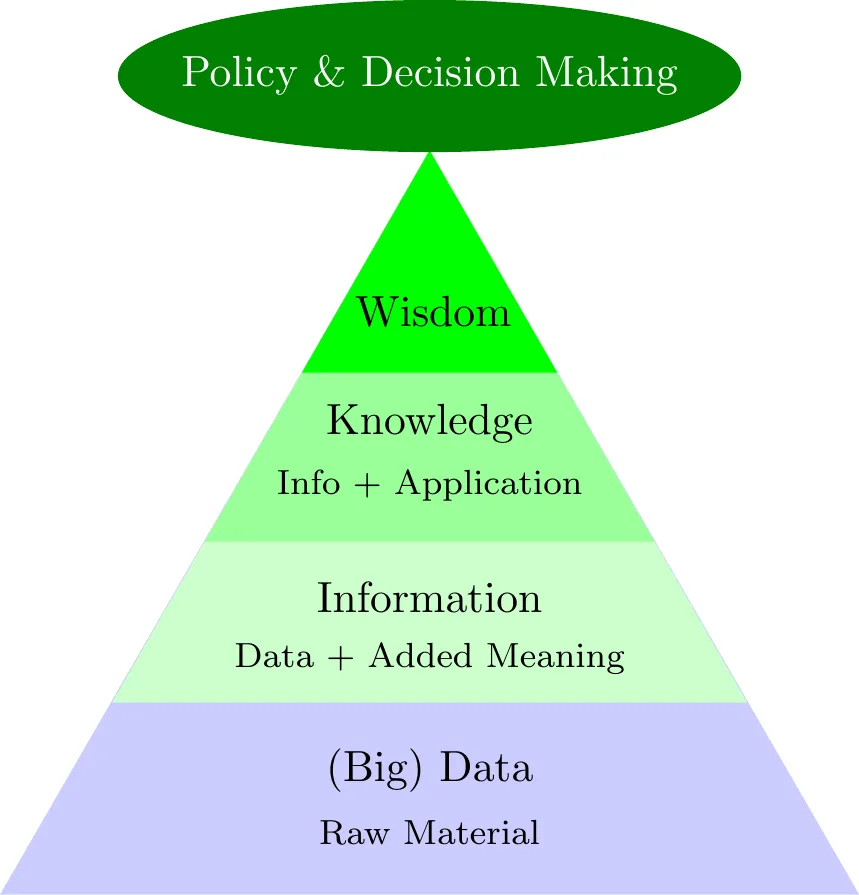
- Turning Data into Information
- Data → Information → Knowledge → Wisdom
- Statistics is the Art and Science of learning from Data.
1.5 Definitions
- Population
- Set of measurements of interest. Characteristics of the population (parameters) are typically of interest.
- Sample
- Subset of measurements of interest. A characteristic of the sample (statistic) is used to infer population characteristics (parameters).
- Parameter
- A characteristic of the population.
- Statistic
- A characteristic of the sample.
- Descriptive Statistics
- Describing the important characteristics of a set of data.
- Inferential Statistics
- Using sample data to make inferences (or generalizations) about a population.
- Statistical Inference
- Making a statement about the population (parameter) based on the sample (statistic).
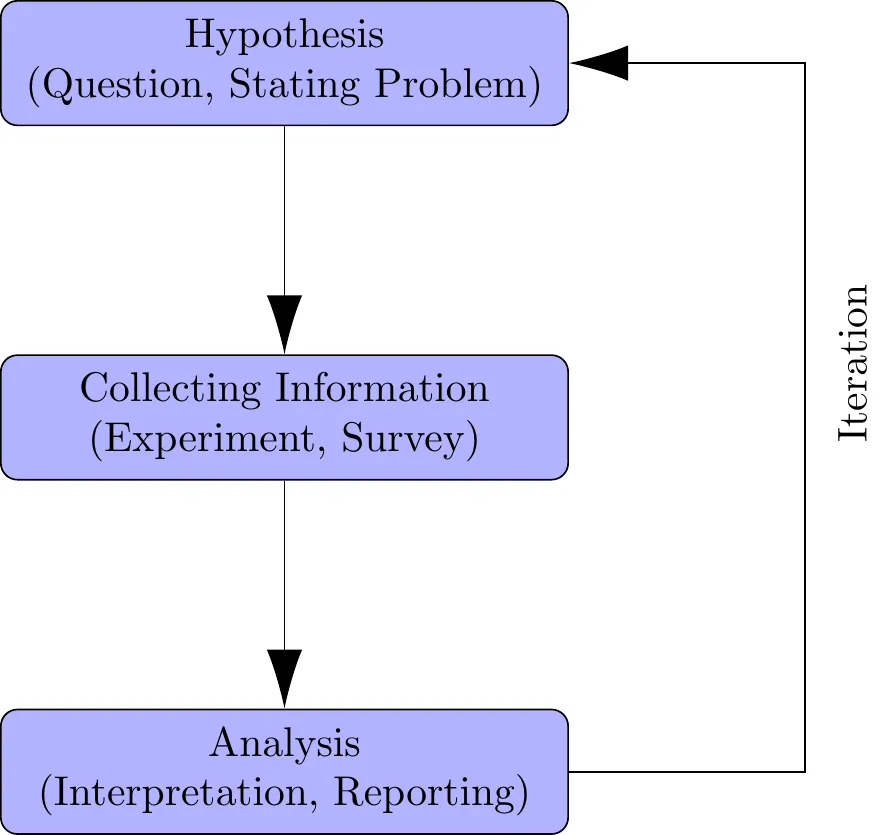
1.6 Scientific Method and Statistics
1.7 Statistical Data Generating Mechanism
1.7.1 Observational Study/Survey
Researcher has (no control) over conditions of interest.
1.7.2 Experiment
Researcher has (control) over some conditions of interest.
1.8 Variable
- A characteristic that may vary from subject to subject
- Height, Weight, Income, Eye color, Gender, etc
- Variables are denoted by last English alphabets in upper case
- X, Y, Z, etc
- Different observations of a variable are characterized by subscripts
- X_{1},X_{2},\ldots,X_{n}, etc
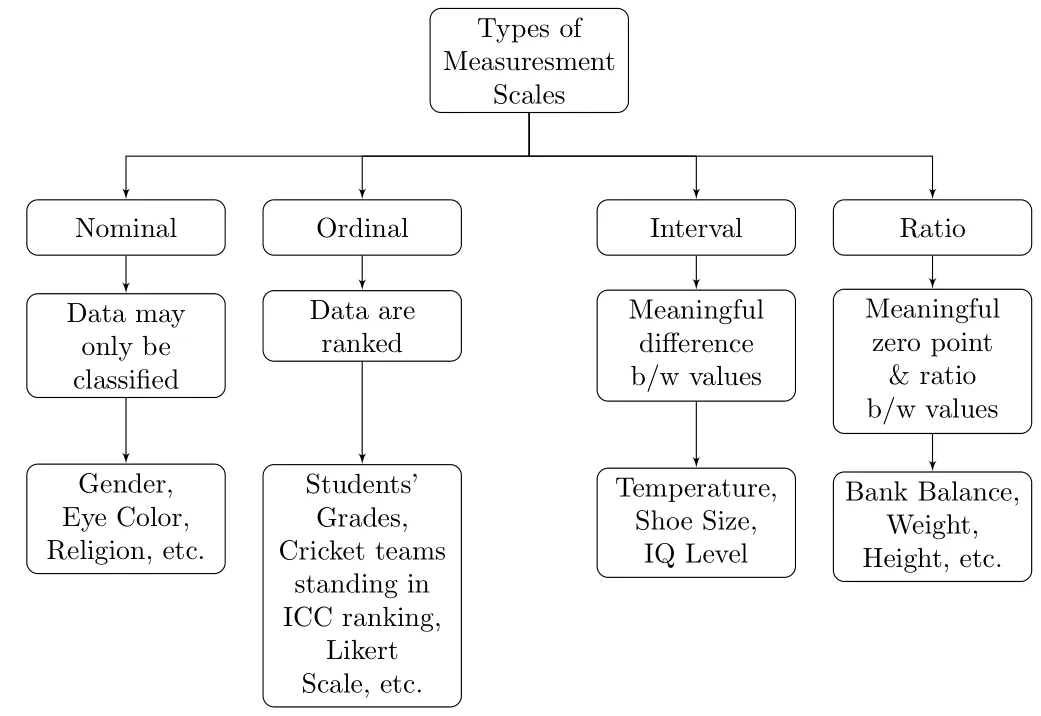
1.9 Measurement & Measurement Scales
- Measurement
- The process of assigning numbers or labels to objects or states in accordance with specific logically accepted rules.
- Measurement Scales
- Data can be classified according to levels of measurement.
- The level of measurement of the data often dictates the calculations that can be done to summarize and present the data.
- It will also determine the statistical tests that should be performed.
1.10 Types of Variables
1.10.1 Qualitative & Quantitative Variables
- Qualitative
- Nominal or Ordinal variables
- Quantitative
- Interval or Ratio variables
- Discrete
- Continuous
- Normal
- Non-Normal
- Interval or Ratio variables
1.10.2 Dependent & Independent Variables
- Dependent Variable
- Variable influenced by other variable(s)
- Independent Variable
- Variable influencing other variable(s)
1.11 Relationship b/w Variables
1.11.1 Dependent & Independent Variables
- Area & Radius of a Circle
- Area of a circle is influenced by its radius.
- Dependent Variable: Area
- Independent Variable: Radius
- Area ← Radius
- Area of a circle is influenced by its radius.
- Electricity Bill & Units Consumed
- Electricity bill is influenced by units consumed.
- Dependent Variable: Electricity Bill
- Independent Variable: Units Consumed
- Electricity Bill ← Units Consumed
- Electricity bill is influenced by units consumed.
- Expenditures & Income
- Expenditures are influenced by Income.
- Dependent Variable: Expenditures
- Independent Variable: Income
- Expenditures ← Income
- Expenditures are influenced by Income.
- Crop Production & Amount of Fertilizer
- Crop Production is influenced by Amount of Fertilizer used.
- Dependent Variable: Crop Production
- Independent Variable: Amount of Fertilizer
- Crop Production ← Amount of Fertilizer
- Crop Production is influenced by Amount of Fertilizer used.
1.12 Types of Relationship
1.12.1 Mathematical Relationship
- Mathematical Relationship
- Exact Relationship
- Y = f\left(X\right)
- Y \mathrel{\color{red}\leftarrow} X
- Relationship between Area and Radius of a Circle
- A = f\left(r\right)
- A = \pi r^{2}
- A \mathrel{\color{red}\leftarrow} r
- Relationship between Electricity Bill & Units Consumed
- \text{Bill} = f\left(\text{Units Consumed}\right)
- \text{Bill} \mathrel{\color{red}\leftarrow} \text{Units Consumed}
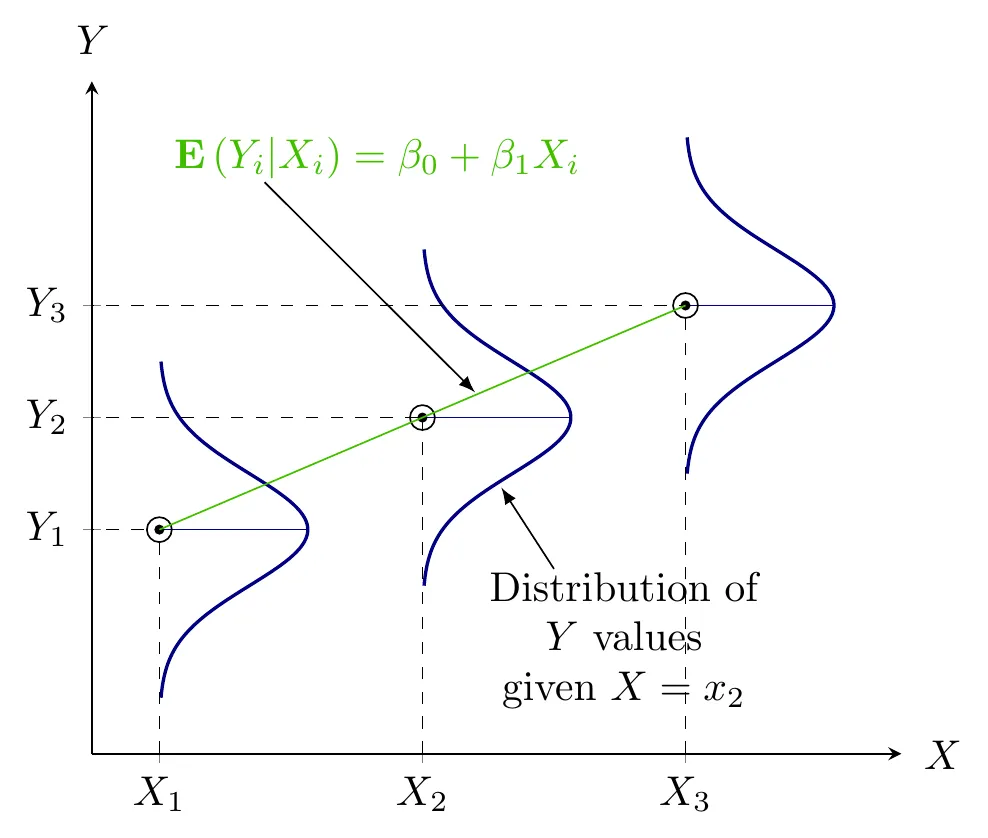
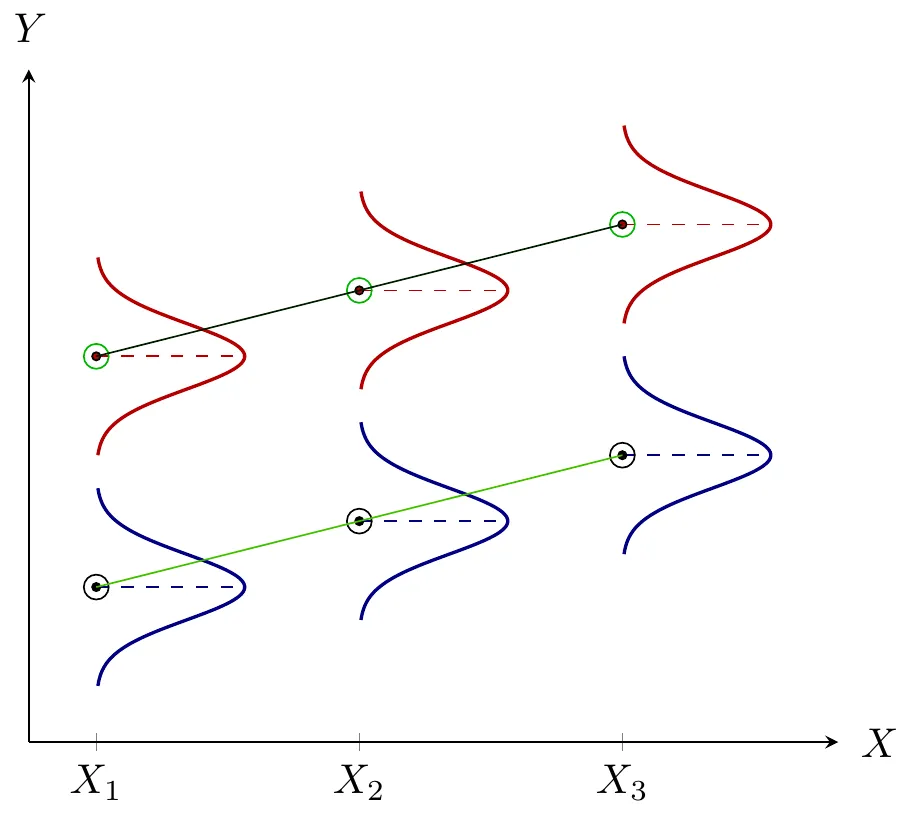
1.13 Statistical Relationship
- Statistical Relationship
- Inexact or Probabilistic Relationship
- Y = f\left(X\right)+\epsilon
- Y \mathrel{\color{red}\leftarrow} X
- Relationship between Expenditures and Income
- \text{Expenditures} = f\left(\text{Income}\right)+\epsilon
- \text{Expenditures} \mathrel{\color{red}\leftarrow} \text{Income}
- Crop Production and Amount of Fertilizer
- \text{Crop Production} = f\left(\text{Amount of Fertilizer}\right)+\epsilon
- \text{Crop Production} \mathrel{\color{red}\leftarrow} \text{Amount of Fertilizer}
1.14 Statistical Models
All models are wrong, but some are useful.
1.15 Linear Model
- Expenditures & Income
- Expenditures are influenced by Income.
- Expenditures ← Income
- Expenditures & Gender
- Expenditures are influenced by Gender.
- Expenditures ← Gender
- Expenditures, Income & Gender
- Expenditures are influenced by Income & Gender.
- Expenditures ← Income + Gender
- Weight Gain & Intake
- Weight Gain is influenced by Intake.
- Weight Gain ← Intake
- Weight Gain & Feed Type
- Weight Gain is influenced by Feed Type.
- Weight Gain ← Feed Type
- Weight Gain, Intake & Feed Type
- Weight Gain is influenced by Intake & Feed Type.
- Weight Gain ← Intake + Feed Type
- Yield & Amount of Fertilizer
- Yield of a crop is influenced by Amount of Fertilizer.
- Yield ← Amount of Fertilizer
- Yield & Varieties
- Yield of a crop is influenced by Varieties.
- Yield ← Varieties
- Yield, Amount of Fertilizer & Varieties
- Yield of a crop is influenced by Amount of Fertilizer & Varieties.
- Yield ← Amount of Fertilizer + Varieties
1.15.1 Regression Model
- Quantify the dependency of a Normal variable on one or more quantitative variable(s)
1.15.2 ANOVA Model
- Comparing means of Normal dependent variable for levels of different factors
1.15.3 ANCOVA Model
- Quantify the dependency of a Normal variable on one or more quantitative variable(s)
- Comparing means of Normal dependent variable for levels of different factors
1.16 R Software
R is a free, open-source programming language and software environment for statistical computing, bioinformatics, visualization and general computing. R provides a wide variety of statistical and graphical techniques, and is highly extensible. The latest version of R can be obtained from https://cran.r-project.org/bin/.
1.16.1 RStudio
RStudio is a powerful integrated development environment (IDE) for R, and it can be downloaded from https://www.rstudio.com/products/rstudio/download/.
1.16.2 Example Code (Minimal)
---
title: "Statistics and the Scientific Method"
format:
html
toc: true
number-sections: true
---
# Introduction
```{r}
#| echo: true
2 + 2
5 - 2
5 * 2
6/2
```